Selection and use of personal protective equipment for medical staff
1. Precautions for the use of medical masks
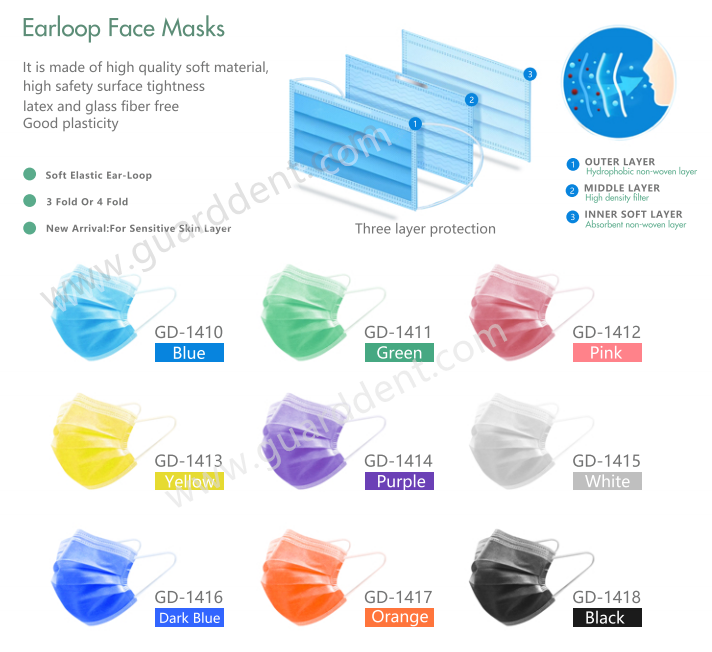
(1) Medical personnel should wear medical protective masks when contacting patients with infectious diseases that can be transmitted through the air or performing diagnosis, treatment, and nursing operations that produce aerosols. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention clearly stated on October 5, 2020 that most of the COVID-19 infections are spread through close contact rather than through the air. Therefore, it is not necessary to prepare medical protective masks for all medical workers who come into contact with patients with COVID-19 . Medical personnel should be required to wear medical protective masks during the diagnosis, treatment and nursing operations of aerosols.
But today, because of Delta spread quickly and infection ability is stronger than COVID-19, It is better for all medical personnel wear medical masks during the procedure.
(2) When working in operating department (room) or caring for patients with low immune function, patients with respiratory infections spread by droplets, operations with body fluid splashing or invasive operations, it is recommended that medical staff wear medical surgery with droplet isolation Facial mask. In general diagnosis and treatment activities, medical staff can optionally wear disposable medical masks or medical surgical masks.
(3) The use of medical masks may lead to changes in the structure of the masks, affecting the close fit between the masks and the face, so they can only be used once. The disinfection method will affect the structure (face fit) and filtration efficiency of the mask. Medical staff are not recommended to reuse disinfected medical masks. Expired medical protective masks cannot be used directly after disinfection.At the same time, it is necessary to test and evaluate whether the structural integrity and filtration performance of the masks meet the product standard of each country.
The face mask standard of each country
In China, it is GB19083—2010 “Technical Requirements for Medical Protective Masks”.
In USA, it is ASTM F2100 Level 1, level 2,level 3.
For Europe, it is EN 14683 Type I, Type II, Type IIR.
In Austrial, it is AS 4381:2015
(4) The filtration efficiency is affected by breathing breath and facial sweat infiltration. Medical masks are generally replaced after 4 hours of wearing; masks found wet during use should be replaced immediately; masks worn should be replaced promptly after being contaminated by patient’s blood and other body fluids.
(5) Medical staff wearing medical protective masks should be checked for “fitness” regularly as required, and the specifications and correct wearing methods of each medical staff’s masks should be determined according to the inspection results.
(6) Medical staff involved in aseptic operations, operations, and intensive care patients should wear sterile masks, check the packaging before use, and use them within the validity period.
(7) Medical staff should choose corresponding medical masks according to the exposure risk of diagnosis and treatment operations and wear them correctly, using one mask each time; wearing multiple masks at a time will not accumulate the protective effect, but will only damage the air tightness of the mask structure and increase discomfort. It is not recommended for medical staff to wear multiple masks at the same time to improve the protective effect.
(8) Protective masks used for the prevention and control of infectious diseases must be removed in a relatively safe area (cannot be removed in the area where protective equipment is removed, otherwise it may cause aerosol transmission risk), and should be used as the last removal protective equipment to avoid removal Pollution that may be caused by the process of other protective equipment.
(9) During the SARS epidemic in 2003, due to the lack of medical protective masks, the World Health Organization (WHO) temporarily recommended medical staff to use N95 particulate protective masks certified by the National Occupational Safety and Health Administration. The surface of the N95 particulate protective mask has no moisture resistance and synthetic blood blocking properties. Therefore, some medical personnel are wrong to regard the N95 mask as a medical protective mask.
(10) The State Food and Drug Administration issued Order No. 319 on May 12, 2003, stipulating that ordinary absorbent cotton gauze masks should not be managed as medical devices, that is, “gauze masks cannot be used as medical personal protective equipment.”
(11) If medical protective masks are not available, medical staff can choose KN95/N95 particulate protective masks and use them with protective masks/face screens. The latter can block body fluid contaminants such as blood that may be splashed on the surface of the mask to avoid impact The filtering effect of the mask.
(12) Medical masks purchased and used by hospitals need to have medical device product registration certification documents and product full performance test reports and save them for future reference.2. Precautions for the use of medical isolation gowns
2. Precautions for the use of medical isolation gowns

(1) Medical isolation gowns are disposable and reusable. Disposable one is more common and widely used than reusable one.
(2) Wear medical isolation gowns when diagnosing and nursing patients with infectious diseases (such as intestinal infectious diseases, multi-drug resistant bacteria infections, etc.) spread through contact or when contacting the living environment of patients; close contact (less than 1 m) Patients with respiratory infectious diseases should also wear medical isolation gowns; when conducting diagnosis, treatment and nursing in protective environments such as bone marrow transplant wards, intensive care and rescue wards, and wards for large-area burn patients, they need to wear sterile medical isolation gowns for protective isolation.
(3) In China, Surgical gowns conforming to YY/T 0506.2-2016 “Surgical drapes, surgical gowns and clean clothes for patients, medical staff and instruments-Part 2: Performance requirements and test methods”, with dry and wet state blocking microbial penetration performance And the specific requirements of water-permeability index can also play the protective effect of medical isolation clothing, and can be used as a substitute when medical isolation clothing is not available.
In USA, Surgical gowns conforming to ANSI/AAMI PB70 “Liquid barrier performance and classification of protective clothing and protective cloth used in healthcare facilities”.
Therefore, when performing operations for patients with COVID-19, as long as they are protected by qualified surgical gowns, medical isolation gowns or medical protective clothing are not required for personal protection.
(4) In view of the transmission route and possible exposure risks of the COVID-19, it is not recommended that medical staff wear waterproof aprons outside the medical isolation gown for enhanced liquid blocking.
(5) Medical isolation gowns purchased and used by hospitals need to have medical device product registration certification documents and product full performance test reports.
3. Precautions for the use of medical protective clothing

(1) There is no difference in the appearance and structure of medical protective clothing and medical isolation clothing, and there are hooded and uncapped ones. The main difference is that the protection requirements for the seams of medical protective clothing are consistent with the overall material requirements, while medical isolation clothing only emphasizes that the seams of key protection areas must have waterproof and antibacterial properties; all seams of medical protective clothing must be glued to prevent liquids Splashes, droplets and aerosols. Therefore, not all Class A or infectious diseases managed under Class A need to use medical protective clothing for protection, such as cholera.
(2) Whether medical personnel use medical protective clothing is related to the level of exposure risk of diagnosis and treatment operations. For example, blocking the liquid transmission of Ebola virus requires medical protective clothing with a sufficient level of protection (Type 3-B and above). The COVID-19 is mainly spread through respiratory droplets and close contact. Contact with virus-contaminated items can also cause infection. Long-term exposure to high-concentration aerosols in a relatively closed environment may be transmitted through aerosols; however, the COVID-19 is transmitted through liquids.
The risk of using medical isolation gowns is low, and the barrier properties of the use of medical isolation gowns are sufficient to protect medical staff from contact with the risk of transmission. The World Health Organization (WHO) does not require medical staff to wear medical protective clothing when contacting patients with COVID-19. If medical staff involved in the operation of patients with COVID-19 wear qualified surgical gowns, they do not need to add medical protective clothing or medical isolation gowns to avoid excessive protection.
(3) Before wearing medical protective clothing, check for damage, and replace it in time if any leakage or damage is found; care should be taken to avoid contamination of hands, face and skin during removal, and avoid dust during removal.
(4) The reusable protective clothing should be cleaned and disinfected in strict accordance with the product instructions, and the cleaning and disinfection methods cannot be changed without authorization, and reused within the number of uses specified in the instructions.
(5) During the Ebola epidemic prevention and control period, Ebola diagnosis and treatment and nursing training camps in Europe used positive pressure protective clothing with positive pressure protective masks. You can pay attention to and understand the performance and use requirements of positive pressure protective clothing.
(6) The medical protective clothing purchased and used by the hospital must have the medical device product registration certificate and the product full performance test report.
4. Precautions for the use of medical protective masks/face screens
(1) The protective mask/face screen should be soaked and disinfected on the spot and then cleaned and disinfected after use. After using a positive pressure protective mask or an electric air-supply filter respirator, use high-level disinfection wipes for surface wiping and disinfection.
When using a positive pressure protective mask or an electric air-supply filter respirator, you should choose a medical isolation gown or protective clothing without a hat; if you are wearing a hooded isolation gown or protective clothing, do not put on a hat, otherwise it will affect the medical isolation gown or Take off the protective clothing.
(2) Before wearing the medical protective mask/face screen, check whether there is any damage and whether the wearing device is loose.
(3) The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention does not recommend the use of goggles because it is prone to contamination of the face and skin during removal. World Health Organization (WHO) experts recommend that the protective mask/face screen and goggles should not be used at the same time.
(4) Medical protective masks/face screens are currently registered and managed as a class of medical devices.
5. Precautions for the use of medical protective gloves
(1) Medical protective gloves must be thin and strong; they must not reduce the touch, affect the flexibility and comfort of the hands, but also have enough length to keep the cuffs of the protective clothing connected to avoid the gloves slipping and exposing the skin during the operation. .
(2) It is not recommended to use multi-layer gloves for protection. If you use double-layer gloves, it is recommended to choose dark-colored gloves for the inner layer and light-colored gloves for the outer layer, so that when the outer layer is damaged, it is easy to find and replace in time.
(3) Gloves must be changed between patients with different diagnosis, treatment and care. After the operation is completed, remove the gloves and perform hand hygiene as required. Wearing gloves cannot replace hand hygiene.
(4) Nitrile gloves can withstand chemical damages such as cleaning and disinfecting agents and are recommended for cleaning and disinfection.
(5) Medical protective gloves are currently registered and managed as a class of medical devices.
6. Medical protective cap

6.1 The protective effect of medical protective caps prevents the head and neck skin and hair of medical staff from being contaminated by infectious substances, and reduces the risk of subsequent contamination to the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth and nose; prevents the spread of microorganisms through dust and dandruff on the hair Contaminate surrounding people, the environment and the surface of objects.
6.2 Selection and use of medical protective caps
6.2.1 The disposable medical protective cap shall meet the requirements of YY/T1642-2019 “Disposable Medical Protective Cap”. It is suitable for medical staff, disease control institutions and other staff when they are in contact with potentially infectious pollutants.
6.2.2 Medical protective hoods can refer to the requirements of the group standard T/CSBME 016-2020 “Medical protective hoods” issued by the Chinese Society of Biomedical Engineering. The protective hood is placed on the head of medical staff and has the functions of masks, eye and nose masks, face masks and other products. It is used to prevent the spread of pathogenic microorganisms from patients to medical staff, isolate and prevent infection.
6.3 Precautions for the use of medical protective caps
(1) Wear protective caps before entering the contaminated area or clean environment and when performing aseptic operations.
(2) Cloth caps should be kept clean, replaced and cleaned every time or every day. Medical staff wearing floral caps cannot go directly to the operating table and must wear disposable sterile medical caps. Disposable medical caps must not be reused. If the medical protective cap is contaminated, it should be replaced immediately.
(3) Medical protective caps are currently registered and managed as a class of medical equipment.
7. Medical protective shoe covers
7.1 The protective effect of medical protective shoe covers prevents work shoes and socks from being contaminated by patients’ body fluids, avoids direct contact with potentially infectious pollutants on the feet and legs of medical staff, and prevents pollution of the clean environment.
7.2 The selection and use of medical protective shoe covers The medical protective shoe covers shall meet the requirements of YY/T1633—2019 “Disposable Medical Protective Shoe Covers”, which are used for medical personnel to contact body fluids, secretions, excreta and vomit indoors. Used for potentially infectious contaminants. When medical staff enter the contaminated area from the potentially contaminated area or enter the ward from the buffer room of the isolation/observation ward, they may consider wearing protective shoe covers.
7.3 Precautions for the use of medical protective shoe covers
(1) The protective shoe cover should have good waterproof performance and be used for one time. Shoe covers made of ordinary non-woven fabrics cannot be used.
(2) Before returning from the contaminated area to the potentially contaminated area, medical personnel should take off the protective shoe covers in the buffer room to avoid contamination of the potentially contaminated area.
(3) If the protective shoe cover is damaged during use, it should be replaced in time.
(4) Medical protective shoe covers are currently subject to record management as a class of medical equipment.
8 .Conclusion
There is no fixed order for wearing personal protective equipment, but it is related to the structure of the protective equipment and personal wearing habits. Each hospital can set the wearing mode according to the type of personal protective equipment configured. It must be ensured that there is no risk of exposure due to contamination during removal, so that the protective mask is finally removed in a relatively safe area. Medical staff must be proficient in the protective effects and use methods of personal protective equipment, combined with their own diagnosis and treatment operational risks, and in accordance with standard prevention, contact isolation, droplet isolation, and air isolation principles, and select appropriate personal protective equipment for effective protection and protection Protect yourself from infection. It is also necessary to avoid excessive protection caused by excessive caution. Excessive protection will not only seriously affect human adaptability and operability, but even reduce the protective effect and increase the risk of infection.
